Dear Aron,
Can I ask, how do you know so much about the Bible? I’ve seen your comments before and I get the impression that you know a lot about theological history too. I’ve always been telling myself I should learn more but I don’t where to start?
Best regards,
Andrew
I’ll save the Church history stuff for another post, and focus on advice on how to read the Bible here.
As for why I know so much about the Bible, well, I’ve been interested in theology since my childhood, so that helps. My Mom was a Sunday school teacher, who talks about the bible all the time, and I also did bible quizzing as a teenager. I’m a fast reader. And ah like to think ah’m purty smart two!
But there are many saints who had none of these advantages, and still knew the Bible like the back of their own hand. God promises wisdom to all those who ask him for it, without doubting. So don’t give up!
In order to learn about the Bible, I think the most important thing is to read it frequently. And, of course, ask the Holy Spirit to teach you how to apply it to your life. Despite what all the pastors say, I’ve never been able to force myself to read the Bible every day (except for a few years in high school, doing the lectionary plan (#4 below) with my mother). Instead I read it in large chunks, and then think about it at other times when I’m walking about or doing other things. If you don’t mind gross metaphors, I guess you could call it “chewing on the cud” like a cow does. I read it first, and ruminate on meaningful verses later. But that doesn’t mean I don’t think about it while I’m reading as well; I’m just looking more at the big picture.
Reading theological commentaries on the Bible is also helpful, but it is not as important as actually reading the Bible yourself. If you want to become very knowledgeable about the Scriptures, the first priority is to actually read the entire Bible. Then do it again. That’ll put you in a better position to judge whether the theologians are bullshitting you or not.
Oh, how I love your law! I meditate on it all day long.
Your commands are always with me and make me wiser than my enemies.
I have more insight than all my teachers, for I meditate on your statutes.
I have more understanding than the elders, for I obey your precepts.
I have kept my feet from every evil path so that I might obey your word.
I have not departed from your laws, for you yourself have taught me.
How sweet are your words to my taste, sweeter than honey to my mouth!
I gain understanding from your precepts; therefore I hate every wrong path.
(Psalm 119 מ (mem))
When you’re reading, first make sure you understand the basic meaning of the text. A Bible with footnotes or study notes may be helpful here, as long as you don’t let it disrupt your flow when you don’t need it. (And as long as the person writing the notes doesn’t have too strong of a theological agenda of their own. The NIV Study Bible notes are definitely Evangelical but otherwise pretty neutral. Avoid the Scofield Reference Bible, which has a complicated “End Times” agenda) Study Bibles also tend to have maps, charts, and introductions to the individual books, which may (or may not) be helpful. If you get stuck, you can also start looking at alternate translations or commentaries.
If you get confused, feel free to slow down a bit and process more carefully. You don’t necessarily need to understand everything, but if you’re reading St. Paul’s letter to the Romans, or something else complicated, you might need to work through the ideas verse by verse just to make sure you understand the basic ideas being expressed. If you do feel you understand the basic literal meaning, then start asking yourself why questions instead. Or ask yourself how it fits into the big context of the whole story of the Bible. In a good Bible study or Sunday school class, people do this together as a group, with an experienced guide.
I never did all that much verse memorization, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t!
But if I partly remember a passage that seems relevant for what I’m thinking about, I always try to look it up immediately (if I don’t remember where it is, using cross-references, Google search, or a concordance). Same thing if I’m reading part of the Bible and it reminds me of another part. Some bibles have “cross-references” to specifically tell you which verses are related to which other verses. Here’s a visualization of a collection of 63,779 cross references, by Sts. Chris Harrison and Christoph Römhild:
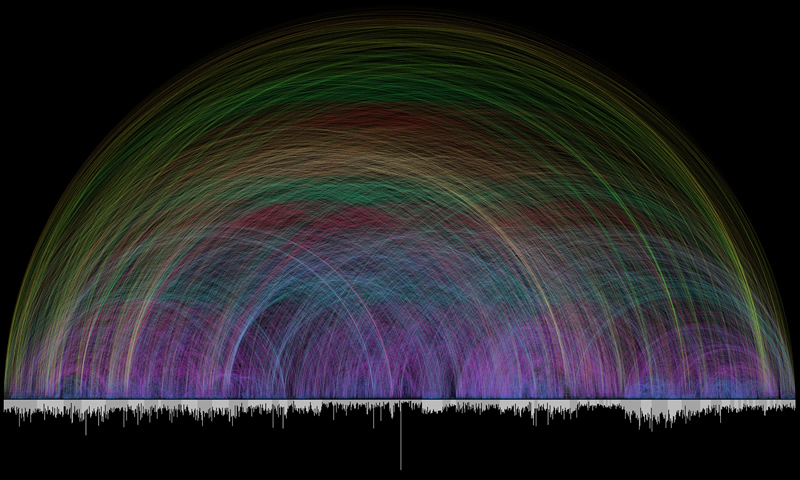
You can see from this that the Bible functions more like a neural network than like an ordinary book. When you know it well enough, it becomes like the third hemisphere of your brain, a bundle of connected ideas which you can use to think, not only about itself, but about other things. It’s your job to figure out what are the cross-references with the things in your own life.
Start by picking a translation which you’re comfortable with. This is a matter of taste, since some translations are more literal, and some are easier to read, and you need to pick the compromise which is right for you. Before you settle on one, check to make sure you like both the way it translates prose (ordinary narration) and poetry (the Psalms and most of the Old Testament prophets).
No translation is perfect, but here are some I can personally vouch for, at a given level of the accuracy/readability tradeoff. In order from most to least literal:
more literal
Shocken Bible (Jewish, preserves a lot of Hebraic style, currently Genesis–Kings only)
New King James Version (or the original KJV if you’re okay with archaic language)
compromise
Holman Christian Standard Version
New International Version (I grew up with this; I prefer 1984 to 2011)
(New) Jerusalem Bible (a Catholic version, I’ve only read the old version)
paraphrase (very readable but not as accurate for serious study)
JB Philips (New Testament only)
New Living Version (this or the Philips are particularly good for Paul’s letters)
Contemporary English Version (very easy to read, particularly good for OT history)
(But I don’t recommend St. Eugene Peterson’s “The Message” unless you are incapable of reading anything not “written up” in bestseller cliches, or have read the Bible a million times before and need an electrical shock. This is in a category of its own, way more nonliteral than any of the other paraphrases. His introductions to the books are pretty decent though.)
I’ve already discussed some of the issues that come up with translation choices before, in my post on why “word-for-word” translations are impossible. If you don’t know ancient Greek or Hebrew, the next best way to “check” a translation you aren’t sure about, is to consult what the same verse says in other translations. If there’s a difference, you know people don’t all agree.
Below are some possible methods for reading through the Bible. I’m basing some of these recommendations off of these suggestions of St. Tim Isbell, the pastor of the church I grew up in.
1) Straight Through
You could just read through all the books in the order they appear in the Table of Contents. But I don’t actually recommend it. First of all, within each Testament, the books are sorted by genre, not always chronologically. There’s nothing theologically special about that order, in fact the Old Testament books appear in a different order in Jewish bibles. In the usual Christian order, the Old Testament is sorted into Torah, History, Wisdom, and Prophecy, while the New Testament has a similar order: Gospels, Acts, Letters, and Revelation.
There’s nothing wrong with reading cover-to-cover if you want to, but there are several disadvantages:
- One is that you won’t get to the New Testament until you’re 3/4 of the way through—which means if you give up early, you won’t get to it at all!
- Another potential problem is that it tends to group similar books together, so you may get bogged down, and it won’t be as interesting as if you mix things up from different parts of the Bible. It’s kind of like eating only meat on Monday, vegetables on Tuesday, fruit on Wednesday, carbs on Thursday, and desert on Friday. It’s better to mix things up a bit.
- Also, some books of the bible have identical or nearly identical passages. For example, the book of Chronicles includes a bunch of summaries of earlier books of the bible, and has chapters which are identical to chapters in Samuel and Kings. Similarly, the three synoptic gospels (Matthew, Mark, and Luke) are all based on a common outline of Jesus’ life. Unless you are specifically interested in comparing-and-contrasting the similar passages, it makes more sense to space these books out, rather than reading them right next to each other.
- Although Genesis and Exodus are mostly pretty interesting, a lot of people get bogged down in Leviticus because of all the weird laws about sacrifices and what to do about leprosy. Personally I find that stuff fascinating, but you might think it’s tedious. This leads to a general rule: if you get bored with anything, go ahead and skim it on your first pass. You can always come back to it again later. Yes, reading the whole Bible is good, but if you aren’t looking forward to reading the next chapter, you might end up putting it off 1 Chronicles 1-9 (nine chapters of genealogy) for months. If you can’t do it, better to keep engaged and moving forward.
2) Arbitrary Order
As an alternative to reading cover to cover, you may wish to simply read the books in a random order, according to your whim and/or the guidance of the Holy Spirit. Once you’ve finished a book, simply mark it with a bullet point in the Table of Contents, so you know which ones are left to read. Then you can try to use up each category of book at about the same time. And you’ll still get the same feeling of accomplishment when you’ve read it all!
3) Storyline Plan
For a first pass through the Bible, you may wish to just focus on the Storyline, the books which contain the main narrative of the Bible.
St. Tim writes that:
If you’ve never read the whole Bible story, or if your grasp of Bible stories is all jumbled, then start with this plan. It is valuable to grasp an overview of the whole Bible – and you can do this reading only the most action-packed 30% of the Bible. The other 70% contains alternative views of the same history, side commentaries written by prophets, and poetry. Reading this 30% of the Bible takes about 30 hours. If you read it like you’d read a novel, in 20 minutes a day you’ll grasp the whole Bible story in just 3 months!
For this you just need to read the following list of books in order:
New Testament:
Any of Matthew, Mark or Luke (your choice).
Acts
Old Testament:
Genesis
Exodus
Leviticus chapter 10
Numbers 9-27
Deuteronomy 27-34
Joshua
Judges
Ruth
1-2 Samuel
1-2 Kings
Jonah
Daniel 1-6
Ezra
Nehemiah
Esther
When you’ve finished, put a bullet point by each of the books you’ve completed. Congratulations, you’re now about 1/3 of the way done with the Bible! When you start reading the other books, you can start by looking at a timeline to remind yourself when they were written, to put them into context.
4) Augmented Lectionary Plan
In this section I will describe my mother’s plan for reading through the entire Bible while simultaneously following the “lectionary readings” associated with each Sunday.
First let me explain what the lectionary is. It’s a rule for deciding which Scriptures to read on a given Sunday. A bunch of liturgical churches in North America, including the Episcopalians, Lutherans, United Methodists, Catholics, etc. have all agreed to use the same cycle of readings, the Revised Common Lectionary (RCL), in their public scripture readings every Sunday.
The readings follow the six seasons of the traditional Christian calender, each of which reflects on a particular part of Christ’s life:
Advent—anticipating the coming of Christ (including the second coming)
Christmas—the Incarnation
Epiphany—Christ revealed publicly
Lent—his life of discipline and self-sacrifice
(culminating in Holy Week, Jesus’ last week, leading up to his crucifixion and burial)
Easter—his resurrection and appearances to the disciples
Pentecost (or Ordinary Time)—his reign in heaven, and continued work through the Church
So if you think it would be cool to have your Scripture readings match what the time of year, and what a bunch of other Christians are reading, this plan may be for you,
In order to cover as much of the Bible as possible, the Lectionary cycles through 3 years, one focussing on each of the 3 synoptic Gospels (Matthew, Mark, or Luke). (The Gospel of John is distributed through all 3 years.) So the cycle approximately repeats every three years, although not exactly due to things like the date of Easter.
Each Sunday has a Gospel and Epistle reading, and usually 2 choices of Old Testament readings, one which goes through the history consecutively, and the other chosen to match thematically with the New Testament reading. When I use this plan, I like reading them both, and also reading any verses they skipped over.
Unfortunately, even in 3 years the RCL doesn’t actually cover the whole Bible, since they tend to focus only on parts suitable for public reading. Worse still, there seems to be a theological agenda to shield congregations from difficult, violent, or upsetting parts of scripture. For example, they often excerpt psalms (unless one is reading Psalm 119, where I understand why people might lose patience, the proper unit of a Psalm is the whole Psalm!) and when they do, it is almost always the violent or cursing parts which they remove. (The most ironic example I know is the reading for Revelation 22:12-14, 16-17, 20-21, which deliberately skips the verse threatening people with Hell. So of course, they also had to skip the verse saying that if anyone removes anything from the book, they’ll be punished with all the plagues in the book. Who knew that liturgists had the same kind of God-defying kahunas that the Pharaoh of the Exodus had?)
On the other hand, churches that read the Lectionary are still exposed to a significantly more diverse set of Scriptures than the average church that doesn’t follow the lectionary. Unless a church takes special effort to include the whole Bible in their worship, they will normally tend to focus on only a very small subset of the Bible; mostly the nicer parts of the New Testament plus a few very selected and stereotypical pieces of the Old Testament.
(And your pastor is definitely not going to impress me with his extensive knowledge of the minor prophets by preaching on Malachi 3:7-12 when he thinks the congregation isn’t tithing enough. I’ve already heard that sermon several times already. If you’re a preacher, why not pick a passage you’ve seldom or never heard preached before? In some ways it’s actually easier to extract the obvious message from a new passage, than to try to say something about the Woman at the Well or the Good Samaritan that nobody’s ever said before.)
Sometimes people say, but doesn’t having a specific scripture for each Sunday stifle the guidance of the Holy Spirit? (In that case, why have a private Bible reading plan either?) My answer: if the Holy Spirit leads you to a particular text, you should definitely listen to that and not do what you were planning to do. But we need a plan to cover the more normal situation, where there isn’t an obvious revelation from God.
Anyway, for those who want to read the entire Bible AND follow the Lectionary, my Mom has created a plan for augmenting the lectionary readings so that you end up read the whole Bible every 3 years. She does it by mixing in readings during the week which go through various books of the Bible. Make sure to read the FAQ as well. The rate is slow enough that if you get off track, you can catch up. This plan is good for people who are already familiar with the main storyline of the Bible, and want to think about the connections between different parts of the Bible.
The next church year starts, not on Jan 1, but THIS UPCOMING SUNDAY (Nov 29, 2015). So if you want to start on this plan, that would be an excellent time to start! But you could jump on board at any time.
5) Chronological Order
You can buy Bibles which purport to put the Scriptures in chronological order. I’ve never read through one of these, but it sounds fun.
It raises an interesting question: do you put the books in the order they were written in, or the order the events described in them happened? (Sometimes these very different, e.g. the Epistles were probably mostly written before the Gospels, but the Gospels describe the life of Jesus which was before when the Epistles were written. Also, sometimes nobody really knows when a text was written, and people are just guessing. So caveat emptor.
6) Anything else
Anything else you want to do? Great! Whichever plan actually gets you reading more of the Bible, that’s the best plan for you! People are welcome to share their own ideas in the comments.
Another idea: if you’re going through the Bible a second time, one way to mix things up is to pick a different translation from your usual choice. Or, you could try to be on the lookout for a particular broad theme (e.g. Messianic prophecies and other foreshadowings of the New Covenant). If your chosen theme is narrower (e.g. biblical feasts and fasts) you might focus on the particular parts of the Bible which are relevant for that theme.
Appendix: A Brief Synopsis of the Bible
A while back I wrote this synopsis of the Bible for a Muslim friend, which I reproduce in a revised form here:
The Old Testament books are sorted by genre (the Jews have the same books but sort them into a different order). The first 5 books are called the Torah, the Pentateuch, or the Law of Moses, and are traditionally attributed to Moses. They are a mixture of narrative and laws:
GENESIS — narrative of Creation, the Fall of Adam & Eve, the flood, God choosing the patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob, and Jacob’s 12 sons who become the 12 tribes of Israel. One of the 12 is Joseph; his brothers sell him into slavery, but Joseph ends up in charge of all Egypt, and rescues Egypt and his family from famine.
EXODUS — The Israelites are oppressed and enslaved, God chooses Moses (and his brother Aaron) to lead them out of slavery, with many dramatic miracles. Introduces the Jewish Passover, the 10 commandments and other laws, construction of the “tabernacle” or tent in which God met them. The Israelites make an idol of the golden calf; God tells Moses he will kill all of them and start over with him, but Moses intercedes by praying to God, and God forgives them.
LEVITICUS — laws concerning priests, sacrifices, clean and unclean animals, and other rituals
NUMBERS — The Israelites wander around in the desert, sinning many times. God tells them to invade the Promised Land (Canaan), but they don’t believe they can do it, and try to stone Moses. Again Moses has to intercede. God makes the Israelites wander around in the desert for 40 years, so that only the children under 20 can enter the land. The people complain of thirst: God tells Moses to speak to a rock and cause water to come out. Moses is so angry with them, he strikes the rock with his staff instead. For this sin, Moses is not allowed to enter the Promised Land.
DEUTERONOMY — Moses delivers more laws as the people are about to enter the Promised Land. Most importantly, to “Hear O Israel, the Lord our God, the Lord is One”, not to make idols, and to “Love the Lord your God with all your heart, soul, and strength”. The death of Moses.
The next set of books are the Historical Books which deal with the history of Israel after the death of Moses. They seem to be partly based on the writings of prophets like Samuel, Nathan, Gad, Ahijah, Iddo, Shemaiah, Isaiah, and Jeremiah, as well as the official court records and other sources. Within this section, the books are in rough chronological order.
JOSHUA — Moses’s assistant Joshua leads the conquest of the Promised Land.
JUDGES — a period of time before there were any kings. The Israelites repeatedly became idoloters, were invaded by foreigners who oppressed them as a punishment, and then were rescued by heroes (called “judges”) chosen by God.
RUTH — a romance story between a Moabite woman named Ruth and an Israelite man Boaz, who marry and become ancestors of David.
1 SAMUEL — the life of Samuel, a prophet who was the last judge of Israel. The people demand a king “like the other nations”. Samuel says that the king will oppress them, and is displeased because God is supposed to be their King. God says to do it anyway, and Samuel anoints Saul as king. However Saul disobeys God & is replaced by David, the shepherd and musician. David serves in Saul’s court, and becomes close friends with Saul’s son Jonathan, but eventually Saul tries to kill David, who runs away and refuses to harm Saul. Saul sins by consulting a medium, and is rebuked by the ghost of Samuel. Saul is then killed in battle alongside Jonathan, and David becomes King.
2 SAMUEL — the reign of David. David serves God with all his heart, and is blessed by God. David decides to build a permanent building for God. The prophet Nathan tells him that instead God will build David’s house, that he will never take away his love from David, that David will have a descendent who will reign forever, and that his son will build a Temple for him. Later, David sins by committing adultery with Bathsheba and killing her husband. Nathan rebukes him, David repents, and God forgives him so that he will not die, but as a punishment tells him that “the sword will never depart from your house”.
1&2 KINGS — The reign of Solomon, a son of David by Bathsheba. God tells Solomon he can ask for anything he wants, and Solomon asks for wisdom. He becomes the wisest person who had ever lived, and builds God’s Temple. He becomes rich and famous and has hundreds of wives. However, in his old age, his wives lead him into idolatry and worshiping other gods, and as a result God divides his kingdom so that his descendents have 2 tribes (called “Judah”) while the other 10 tribes become a different country (called “Israel”). The book goes on to describe the kings in Judah (some of which followed God) and the kings in Israel (who nearly all didn’t). The prophets Elijah and Elisha protest against the wicked king Ahab in Israel. After several more generations, Assyria conquers Israel. Later Babylon captures Judah, and leads the Jews into captivity for 70 years, as prophesied by Jeremiah.
1&2 CHRONICLES — another perspective on the same history.
EZRA & NEHEMIAH — After the Persians conquered the Babylonians, they allowed the Jews to come back and rebuilt their Temple and city wall. Under the influence of the righteous priest Ezra, the Jews commit to follow only God and to obey the Law of Moses.
ESTHER — The Persian King Xerxes takes a Jewish girl as his Queen. She courageously intercedes to prevent a genocide of the Jews plotted by Xerxes wicked advisor Haman.
The next set of books are called “Wisdom Literature” because they include practical perspectives on what life is like:
JOB — a dialogue about a righteous man Job, who is very rich and prosperous. God allows Satan to take away everything he owns, to kill his children, and to afflict him with a horrible disease, to see if he will still serve God. Job’s 3 friends come and tell him he should repent because he must have sinned. Job argues with them, saying he was righteous and complains bitterly against God, and asks God to vindicate him. At the end, God comes down and, instead of explaining himself, asks Job questions about Nature which he can’t answer, and Job cannot reply. Finally, God says that he is angry with Job’s friends “because they did not speak rightly about me, as my servant Job has”, and requires that Job offer sacrifices for them so that they can be forgiven. God restores Job’s wealth to twice what it was before.
PSALMS — a book of 150 hymns (songs) for the Temple worship, about half by King David and the rest by other people. Mostly prayers of human beings to or about God.
PROVERBS — advice about living a good life, mostly short sayings by Solomon and others.
ECCLESIASTES — philosophy attributed to Solomon about how earthly life is meaningless, so you should find contentment wherever you can, while still obeying God.
SONG OF SONGS — erotic poetry celebrating love, also attributed to Solomon.
The final set of Old Testament books are called the Prophets (even though obviously prophets were involved in the other books too, these books are usually involve the message of God given to a single, specific prophet):
The “major prophets” (called that only because their books are longer than the others, not because they are necessarily more important) are ISAIAH, JEREMIAH, EZEKIEL, and DANIEL. Of the 12 “minor prophets”, the first 9 are HOSEA, JOEL, AMOS, OBADIAH, JONAH, MICAH, NAHUM, HABAKKUK, and ZEPHANIAH. These prophesied before or during the Babylonian exile, warning the Israelites that they would be punished for their idolatry. The nations would then be punished for their sins, and finally God would restore Israel under the reign of the Messiah, David’s descendent, who will cause all nations to worship the one true God, and will reign forever. The last 3 minor prophets, HAGGAI, ZECHARIAH, and MALACHI, were sent to encourage the people after they returned from exile, in the Ezra-Nehemiah period. Malachi was the last prophet of the Old Testament, after than there was a silence of no prophets for 400 years, before the New Testament.
[Catholics accept a few additional books in the Old Testament beyond those listed here. These were written in the Intertestamental Period: after the prophesy of Malachi, but before the birth of John the Baptist. They are not included in most Protestant or Jewish Bibles. Among them, the books I’ve found most interesting are 1-2 Maccabees which provide some useful historical context for this period, and Wisdom and Sirach (a.k.a. Ecclesiasticus) which are additional books of wisdom/proverbs. The others are Tobit and Judith (fictional historical romances with obvious anachronisms), Baruch (supposedly written by Jeremiah’s secretary) and various Additions to the books of Esther and Daniel. The Orthodox accept a few more. But I wouldn’t worry about any of these until you’ve read the books that all Christians accept!]
The New Testament:
This begins with the 4 Gospels of MATTHEW, MARK, LUKE, and JOHN which are biographies of Jesus, the descendent of King David. Beginning with the ministry of John the Baptist, and Jesus’ Baptism, they go on to describe Jesus’ teachings and miracles. Then comes the Passion, in which Jesus entered Jerusalem, was betrayed to the Jewish and Roman leaders, condemned for our sins and crucified. Then he came back to life again, and appeared to his disciples after the Resurrection, commissioning them to preach the gospel to all nations.
St. Luke also wrote a sequel called ACTS (short for “Acts of the Apostles”) which describes the early Church after Jesus’ ascension into heaven, and how the Holy Spirit came to live inside of every person who believes in Jesus as the Messiah. It also tells about the ministries of the apostles St. Peter (Jesus’ disciple) and St. Paul (who persecuted Christians until he had a vision of the resurrected Jesus appearing to him). It describes a vision in which Peter saw a sheet come down from heaven, and to kill and eat unclean animals. Peter protested, but the vision was repeated 3 times. The point of the vision was to explain how God was now going to accept non-Jewish people into the church. It is also why Christians do not have dietary restrictions about clean and unclean animals, like Jews and Muslims do.
Then there the letters (called “Epistles”) which give practical instructions for living the Christian life, as part of the Church, in light of the salvation that has come to us through Jesus. There are 13 letters by Paul to different churches or individual Christians (ROMANS, 1-2 CORINTHIANS, GALATIANS, EPHESIANS, PHILIPPIANS, COLOSSIANS, 1-2 THESSALONIANS, 1-2 TIMOTHY, TITUS, PHILEMON), plus HEBREWS, an anonymous letter to Jewish Christians which was traditionally attributed to Paul but most scholars think it was probably written by someone else in his circle. There’s also 1 letter by JAMES (Jesus’ brother), 2 by PETER, 3 by JOHN, 1 by JUDE (another brother of Jesus). These letters describe the theology and practice of the apostles, and we regard them as inspired because Jesus promised that the Holy Spirit would guide the apostles.
Finally, there is a book called REVELATION (“The Revelation of Jesus Christ”) which involves prophecies about the end of the world (among other things), attributed to St. John in his old age.

